
How and why use renewable energy?
The mining and blockchain industry can be environmentally friendly without compromising profitability. If you want to find out in what way, this blog will tell you about GRN Association and their vision.
The blockchain industry has had a bad reputation since its inception due to its excessive use and consumption of energy.
Current blockchain designs run on algorithms that can consume up to 215 kWh per transaction (i.e., the equivalent of letting an incandescent light bulb of 25W burn for a whole year). The reason is that validating and securing transactions on the blockchain requires enormous computing power.
For example, the servers that run bitcoin's software are estimated to use at least 22 terawatt-hours (TWh) per year, which is almost the level of Ireland's annual electricity consumption.
In addition, an expansion of blockchain will require additional "data mining" and, consequently, additional energy consumption. Several green-mining solutions that use renewable energy sources and more energy-efficient hardware are currently being tested. One example is the green-energy startup Hydrominer, which operates two hydropower mining farms in the Austrian Alps.
The resulting e-waste, along with other shortcomings, prevent farms from acting as a viable alternative to the current centralized system or for wider adoption.
GRNGrid, an initiative of GRN Association, whose mining process is characterized by sustainability, has found solutions to all these unresolved environmental issues.
GRNGrid's story began when energy efficiency in data centers was one of the most important issues facing IT professionals and their clients. A group of visionaries stands by the fact that cryptocurrencies have a future only if renewable energy resources are used. When they started a company, the main goal which has guided them over the years was the solution to problems related to ecology by introducing the Grid blockchain and its native token GRN (pronounced Green) using its new and unique Proof of Stake v2 algorithm.
GRNGrid’s story began when the founders of GRN-Energy, together with some crypto professionals, started thinking of a way to make blockchain more sustainable: if mining is necessary, it’s important to use renewable energy (the same counts for running the nodes). And to do so, a new sustainable first blockchain needed to be designed, sparking the creation of Proof of Stake V2. To guarantee a decentralized project, GRN ($G) was the logical next step to fund the project.
The token is designed to be an energy-efficient, high-performance, low-fee smart chain that actively supports decentralization and security. Their technology enables green transactions, and they are probably the first smart chain to be created with the ability to work based on renewable energy sources.
Furthermore, GRNGrid incorporates several valuable features such as an integrated payment and deposit system, swapping pools, and encrypted chat between users. The functionality itself does not require anyone's permission, and Grid validator nodes are decentralized and permissionless. In other words, it provides resilience for the future and makes no compromises while staying sustainable.
You've probably heard about "being green" before, and you're wondering why. Here are some answers.
Why be "green"?
Let's briefly repeat that renewable energy is produced from sources like the sun and wind that are naturally replenished and do not run out. Renewable energy can be used for generating electricity, space and water heating and cooling, and transportation.
Non-renewable energy, in contrast, comes from finite resources that could get used up, such as fossil fuels like coal and oil.
Renewable energy availability changes how we operate modern mines, fuel, and cars and how we supply nearby communities with heating and cooling.
This type of energy represents an affordable choice for miners, who use it to crush, dig, and process minerals. Renewables ("green energy") are generated from sources that replenish over time. The most common uses of renewable energy in the mining industry involve:
- Wind;
- Solar;
- Biodiesel;
- Geothermal energy;
- Hydropower;
- Hydrogen and fuel cell energy.
Not only are renewables mitigating the effects of pollution, but they are also making sure new technologies function sustainably in the mining industry.
Advantages of renewable energy
The advantages of renewable energy are numerous and affect the economy, environment, national security, and human health. Here are some general benefits of using renewable energy:
- Enhances reliability, security, and resilience of the nation's power grid;
- Job creation throughout renewable energy industries;
- Reduced carbon emissions and air pollution from energy production;
- Increases energy independence;
- Increases affordability since many types of renewable energy are cost-competitive with traditional energy sources;
- Expands clean energy access for non-grid-connected or remote, coastal, or islanded communities.
Renewable energy technology is also affecting and changing the mining industry for the better in many ways:
- Cheaper mining operations;
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions;
- Sustainable development support;
- Energy efficiency on mine sites.

Barrage and GRN Association enjoying the greenery in Osijek
4 ways the mining industry uses renewable energy
Solar energy
It is known that some miners gradually switch to solar energy. Solar energy uses the sun's radiation to create concentrated solar power (CSP) or photovoltaics (PV), which are one of the most sustainable sources of energy.
With its low cost, solar energy does not contribute to the environmental risks associated with nuclear power, water pollution, nitrogen oxides, and other harmful waste.
Wind energy
One of the most popular ways to produce electricity is definitely the energy of wind, which converts kinetic energy sources into mechanical ones.
In fact, the total capacity of wind turbines installed in 2018 reached 597 gigawatts (GW), according to data from the World Wind Energy Association.
The wind is also powered by direct sunlight and is used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in mines. The energy produced can be used to send power over the grid for several types of mining operations.
Water
Water conservation uses cutting-edge technology since water is an important resource for mining natural gas, coal, oil, and uranium.
Fuel extraction from mine sites produces toxic wastewater. However, reprocessing nuclear or old coal plants with more water treatment technologies helps to minimize the number of fuel withdrawals - making it better for the environment.
Beyond the relationship between water and energy, the choices we make today will determine how we face the growing demand of the future.
Renewable energy powers machinery and operation sites
Renewable energy technologies enable us to create more effective ways to generate electricity for use in mines. The use of renewable energy applies to innovative ideas like:
- Electric Vehicles
- Hybrid power plants
- Microgrids and Artificial intelligence (AI)
- 3D Printing
- Bladeless wind turbines
- Hydraulic mining
Renewable energy solutions have supported millions of communities across the globe, allowing corporations to operate in harmony with the natural world. As we continue to expand towards more conscientious resources, the mining industry is now able to carry out smarter policies, invest in cleaner solutions, and support further research to embrace its cause, which is one of GRNGrid’s goals.
What does the GRNGrid stand for?
The project itself is an initiative by GRN Association to tackle environmental pollution problems that came as a result of the current Blockchain industry and technology.
GRNGrid is focused on working with clients and business partners that can identify themselves in their simple philosophy - creating value and generating sustainable profit.
They believe their philosophy attempts to protect the coming Web 3.0 and blockchain adaptation and innovation against regulatory changes and economic disruption and ensure it has a sustainable impact.
One of the main missions is building, investing in, and providing sustainable Web 3.0 and computing solutions as a catalyst for creating economic development, reducing e-waste, and building a circular economy for society and the long-term benefits.

A workshop session at Barrage’s conference room
GRNGrid is an energy-efficient smartchain with high performance and low costs.
Grid’s objective is to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy in blockchain technology and to provide every company and person with the opportunity to “go green” as soon as WEB 3.0 is universally embraced. Additionally, the progressive distribution of GRN for validation supports sustainable development and discourages wealth buildup. These characteristics position GRN as a viable alternative to existing (de)centralized technology.
As mentioned before, GRNGrid is a ground-breaking blockchain technology built on the Proof of Stake v2 consensus mechanism.
The original Proof of Stake is hailed for effectively reducing the energy consumption needed to keep the blockchain running. Unfortunately, Proof of Stake introduces two major problems:
1. Those with a higher stake get the majority of the rewards. Eventually, lower staking validators are driven away as it becomes less profitable to run a validation node.
2. Project owners often have the highest stake, especially at the starting phase, in the circulating supply, rendering them the de facto chain owner.
These problems make the PoS consensus method resemble a centralized system. Furthermore, the chances for a 51% attack still remain.
The GRNGrid implements a brand-new consensus technique called Proof of Stake v2 to protect the network against the 51% attack and to address these issues.
This consensus works in two steps:
- It generates a random selection of validations for a security pool. The selection criterion for a particular security pool is a decreasing concave function on the validator’s staked quantity. The security pool reduces the likelihood of whales being grouped in a single security pool. This is an additional safeguard to protect the Grid from whale validators attempting to control the system and prevent validator cartels from forming. This strategy promotes the involvement of other validators. Validators with a lower stake are more likely to be picked to join a security pool, hence boosting their payout.
- A decreasing concave function assigns voting right for validator j in the security pool i. The consensus method is evaluated using three different settings:
a) attacker holding 80% of the stake;
b) attackers holding a combined 90% of the stake;
c) attacker holding the minimum required stake but having 51% of the total GRN validators.
The Proof of Stake v2 showed a 0.0000% chance of a successful attack in all these scenarios.
Grid will mainly focus on:
- Setting a framework for creative corporate solutions;
- Consumer usability;
- Deployment and development of WEB 3.0 applications;
- Sustainability of blockchain.
The grid will introduce the main novel features to better compete with (de)centralized technologies like:
- EnScrypt;
- ExNode;
- GRNPay.
EnScrypt
EnScrypt will allow users to send encrypted messages up to 120 characters attached to a transaction or as standalone messages. These messages can be an invoice number, payment reference code, or simply a friendly note.
ExNode
ExNode represents the first integrated DEX-based exchange on the blockchain. Grid users can stake or swap their tokens to any (stable) currency on Grid without ever requiring making a transaction to any exchange. This integrated swapping also makes it possible to easily stake any token running on the Grid from the GRN wallet app.
EXNode is supported through the GRN wallet app or any other third-party wallet app connecting to the EXNode contract addresses.
GRNPay
With GRNPay, users can send and receive payment requests over Grid, which can be accompanied by EnScrypt messages. Paying for the requests can be easily done with the wallet app, and the recipient will immediately be notified once its payment request is fulfilled. The payment requests can be set in any currency and be paid in a whole different currency, as EXNode will manage the conversion to match the recipient’s currency.
GRNPay can also be used as an Escrow service between businesses. GRNPay can reserve the currency on the sender’s address until a pre-set condition is satisfied. GRNPay will automatically credit the recipient.
In line with the technicalities of the platform, GRNPay services are hosted decentralized and permissionless on the GRNGrid and are based on automatically issued smart contracts.
What does the GRN token stand for?
The token GRN (GRN is pronounced “Green”) and the sustainable blockchain GRNGrid were introduced at the initiative of GRN Association to tackle the environmental polluting problems. The GRN token serves multiple use cases in Grid, including staking, paying for fees, and validators incentives.
Furthermore, the GRN token is also used to promote the adoption of renewable energy by the usage of the GRN token in the operations of a renewable energy and mining company.
GRN ($G) will serve as the native token on the Grid and will primarily be used for:
- Paying for transaction and computing fees;
- Validation and staking rewards;
- Voting for features;
- Shopping on the Grid (NFTs).
Every prospective validator must also stake a specified amount in Grid’s security pool to qualify as a validator. GRN is the primary currency used in Grid-based smart contracts and will serve as the primary pool token in EXNode.
In addition, GRN is a utility token that can be used for payment to access the corporate services of GRN Energy and some of their partners in the renewable mining sector after it has become tradeable. This use case provides GRN with a stable and considerable demand, ensuring safety from heavy price fluctuations from day one.
GRN token is possible to buy on LBank, Bitmart, LAtoken, and XT.com.
Token info:
- Ticker: GRN
- Token price in USD: 1 GRN = 0.18 USD
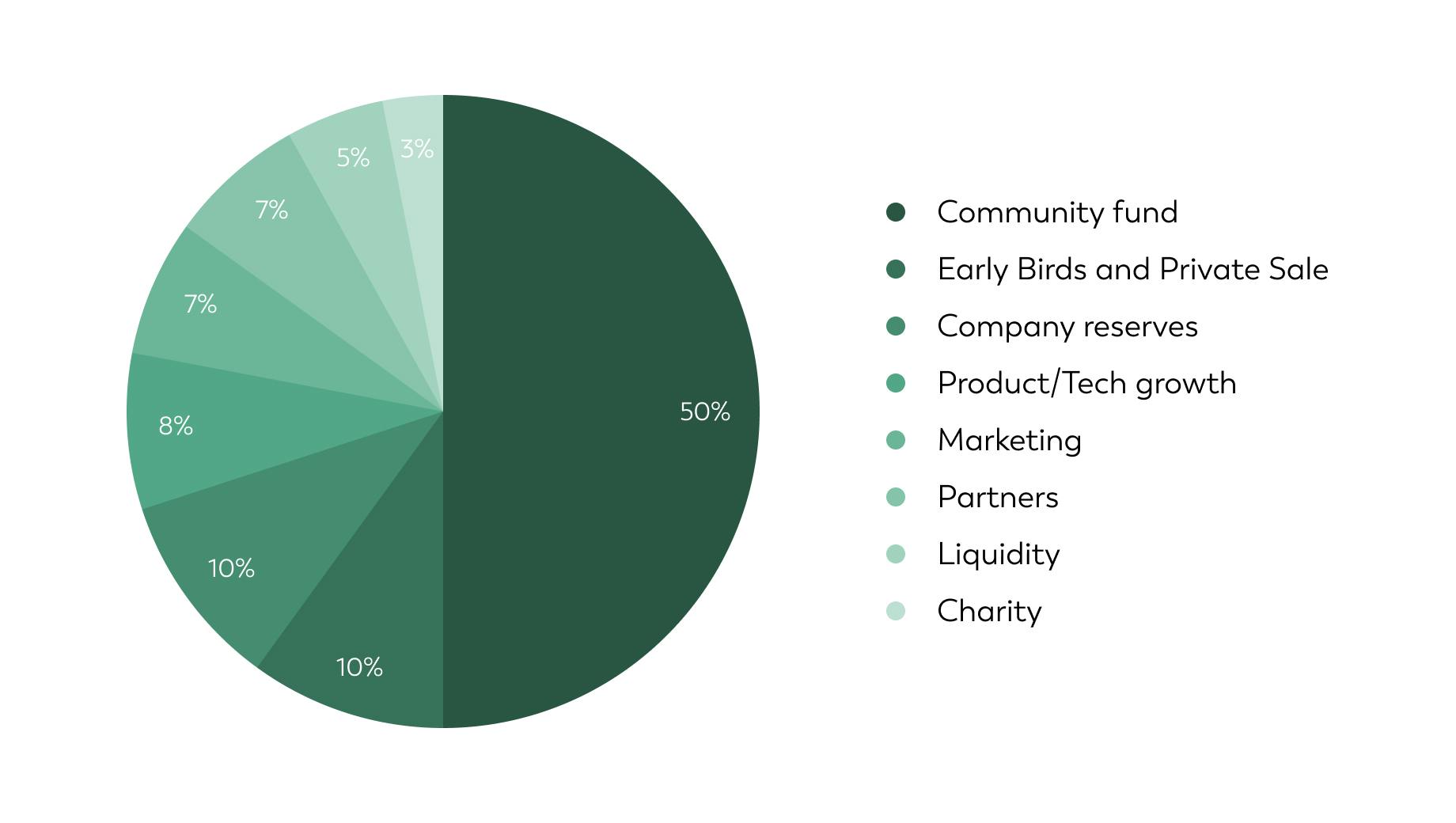
Token distribution:
- Community fund - 50%
- Early Birds and Private sale - 10%
- Charity - 3%
- Liquidity - 5%
- Marketing - 7%
- Company reserves - 10%
- Product/Tech growth - 8%
- Partners - 7%
Why is the GRNGrid “greener”?
The blockchain industry will be the future of renewable energy and the next chapter in smart technology, as the online platform is helping develop consumer-driven power generation.
Today’s technology is providing a new level of sophistication to our energy supplies which have previously been reliant on highly centralized systems. The potential opportunities are endless, and by increasing efficiency, blockchain could also allow for a substantial reduction of carbon emissions.
As mentioned, today’s technology and awareness of the environmental issues in the world can reduce wasteful use of power and resultant e-waste.
Since awareness has crossed all boundaries, many companies are using blockchain in innovative ways to improve how we interact with our energy systems. Here are some:
- WePower (Estonia)
Estonia’s 100% digital energy grid made implementing a blockchain platform easy for WePower. The startup joined forces with an independent energy provider and gave consumers a chance to buy into their program using their own cryptocurrency. Blockchain offers WePower a transparent platform on which consumers can monitor energy prices and adapt and diversify their energy portfolio based on their predictions. In their white paper, WePower explains that they see blockchain and renewable energy as the next power couple in the energy market - both being complementary.
- Power Ledger (Australia)
Australia has long been recognized as a country with immense potential as a clean energy hub. As blockchain rose as a platform for change, Australian startup Power Ledger jumped at the opportunity to help develop the country’s renewable energy market whilst also being able to offer lower prices to local consumers. With a rapid increase in personal solar power generation amongst Australian households over the past decade, Power Ledger recognized the conundrum facing the country’s energy suppliers: what happens when clean energy powered by individuals becomes cheaper than their own fossil fuel, which is burning plants in the process?
- Acciona Energy & Iberdrola (Spain)
Both Acciona Energy and Iberdrola have used the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) as the framework for their clean energy program and hope to help Spain transition away from fossil fuels. As two of Spain's largest energy companies, they have an opportunity to implement blockchain quickly with a large-scale impact. Acciona Energy became the first utility company to use blockchain technology to certify the origin of its energy to consumers, while Iberdrola used a similar platform in its own pilot program.
- The Brooklyn Microgrid (United States)
The Brooklyn Microgrid is a community-based approach to blockchain. It reimagines the traditional energy grid model with the concept of a communal energy network. While the utility provider still maintains the electrical grid that delivers power, the actual energy is generated, stored, and traded locally by members of the community for a more resilient and sustainable clean energy model.
- The Sun Exchange (South Africa)
The Sun Exchange is a startup that focuses on investment-driven solar installations. It identifies sun-soaked areas in South Africa where solar panels could be at their most efficient, then sells the modules to private investors who can then lease them to local schools and businesses.
This business model ensures that local communities can benefit from cheap, clean energy whilst investors help fund and develop several projects that will generate income for the twenty years that solar panels are viable. All transactions can be processed via bitcoin, simplifying international monetary transactions, and the Sun Exchange uses blockchain-based smart contracts to reduce the needs and cost of physical administration.
What are the specific advantages of the GRNGrid?
The GRNGrid project is a sustainable improvement to the third generation of the blockchain industry. GRNGrid is a blockchain with endless possibilities and zero compromises.
It is designed to be an energy-efficient, high-performance, low-fee smartchain that actively supports decentralization and security; also, Grid emerges as the first smartchain to be created with the capability of operating entirely on renewable energy sources.
The GRN token serves multiple use cases in Grid, including staking, paying for fees, and validators incentives. Furthermore, the GRN token is also used to promote the adoption of renewable energy by its use in the operations of renewable energy and mining companies.
Grid’s main goal is to adopt renewable energy in blockchain technology and to provide every company and person a concrete opportunity to “go green” as soon as WEB3.0 is universally embraced.
Since we are highly experienced and expertized in and off blockchain software solutions, we would proudly announce that we will participate in this project and give our best to provide valuable input in creating the visual identity, branding, user experience, interface design, and web application development of Grid and GRN wallet.
All the details about the GRNGrid project you can find on their official website, and you can follow and support their work on social media platforms Youtube channel, Telegram, LinkedIn, Twitter, and Discord.
We are extremely looking forward to working together, achieving common goals, and everything that will come in the near future with developing and testing Grid and the GRN wallet.
Your take on the subject
They say knowledge has power only if you pass it on - we hope our blog post gave you valuable insight.
If you want to share your opinion or learn more about green energy sources and sustainable but decentralizing blockchain technology ideas, feel free to contact us. We'd love to hear what you have to say!